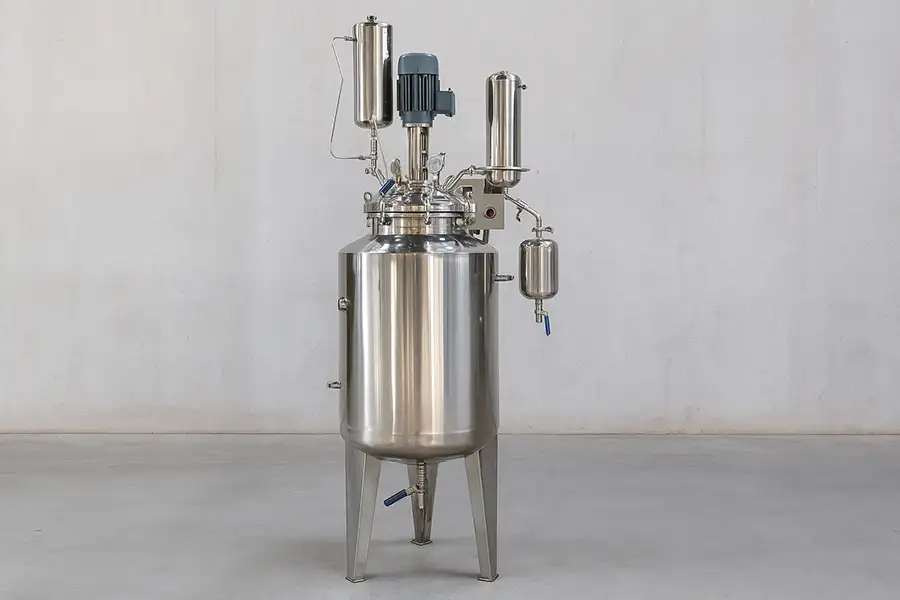
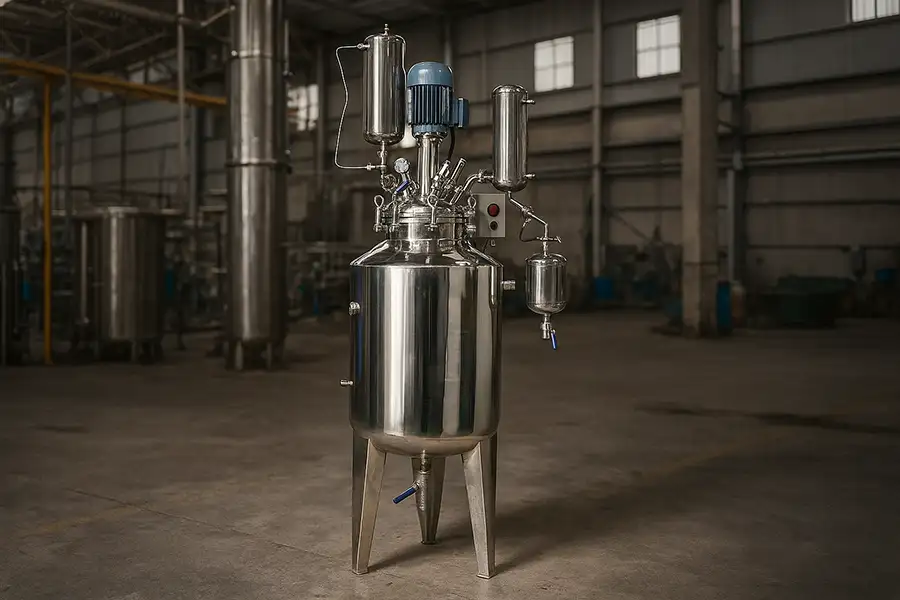
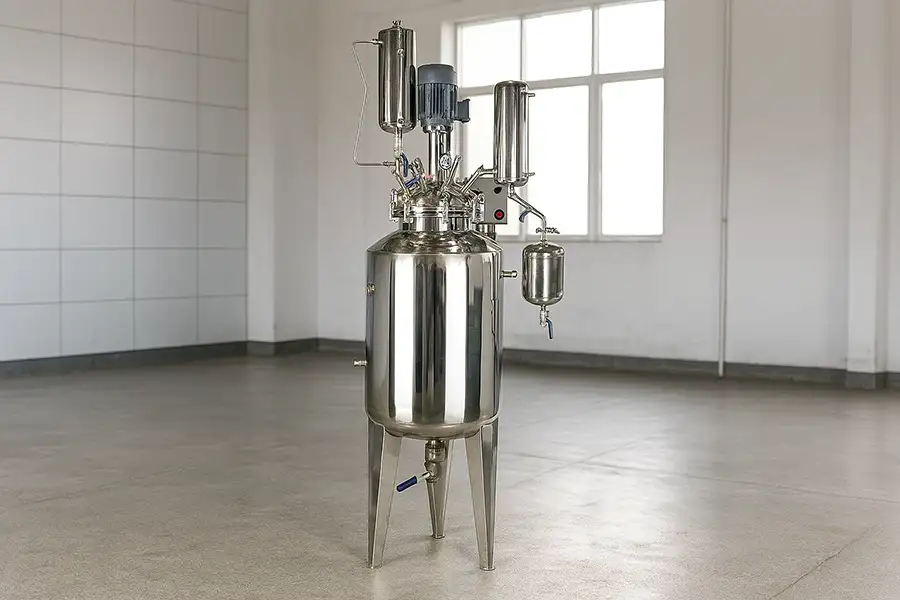
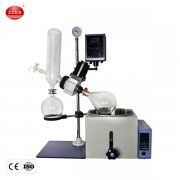
In modern chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries, the stainless steel chemical reactor plays a pivotal role in ensuring safe, efficient, and precise chemical processes. These reactors are specialized vessels designed to handle chemical reactions under controlled temperature, pressure, and mixing conditions.
Stainless steel, particularly grades like SS304 and SS316, is the preferred material choice for such reactors due to its high corrosion resistance, excellent mechanical strength, and ability to withstand varying temperatures. According to data from the International Stainless Steel Forum (ISSF), the demand for stainless steel in the chemical industry has grown by over 4% annually over the past decade, highlighting its critical role.
How Does a Stainless Steel Chemical Reactor Work?
At its core, a stainless steel chemical reactor is a container where raw materials are combined to undergo a desired chemical transformation. These vessels may operate under atmospheric, high-pressure, or vacuum conditions depending on the process requirements.
-
Mixing: Reactors are equipped with agitators to ensure uniform mixing of components.
-
Heating and Cooling: Jackets or coils allow for precise temperature control.
-
Pressure Control: Designed to withstand specific pressure ratings for safety and efficiency.
What makes stainless steel better than other materials for chemical reactors?
Stainless steel offers superior resistance to corrosion, especially in acidic or alkaline environments, and does not contaminate the product—critical for pharmaceutical and food-grade processes.
Advantages of Stainless Steel Chemical Reactors
Some notable benefits include:
-
Corrosion Resistance: Significantly extends service life.
-
Temperature Tolerance: Handles both cryogenic conditions and high heat.
-
Hygiene: Easy to clean, meeting stringent GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) standards.
-
Structural Strength: Maintains integrity under high pressures.
Can stainless steel reactors be customized for specific industries?
Yes, customization is common—adding features like specialized agitators, baffles, high-pressure jackets, or integrating sensors for pH, temperature, and viscosity measurements.
Applications in Different Industries
Stainless steel chemical reactors are widely used in:
-
Chemical manufacturing – synthesis of polymers, resins, and other compounds
-
Pharmaceutical industry – production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)
-
Food and beverage – brewing, dairy processing, and flavor production
-
Cosmetics – producing emulsions, creams, and lotions
Design Considerations
When selecting a reactor, key considerations include:
|
Factor |
Importance |
Example |
|
Material Grade |
Determines corrosion resistance |
SS304 for general use, SS316 for high chloride environments |
|
Capacity |
Matches production volume needs |
From small lab units to multi-thousand liter vessels |
|
Pressure Rating |
Safety and process suitability |
Design codes like ASME standards |
Market Trends and Data
Based on research from MarketWatch, the global market for industrial chemical reactors—including stainless steel models—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5% through 2030. This growth is driven by expanding chemical production and stricter quality standards.
Interestingly, according to a study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), by 2030 automation and AI integration in manufacturing could replace up to 30% of manual monitoring roles in process industries—meaning future reactors will likely come with advanced automation features.
Related Resources
For readers interested in related processing equipment, check out:

 Products
Products