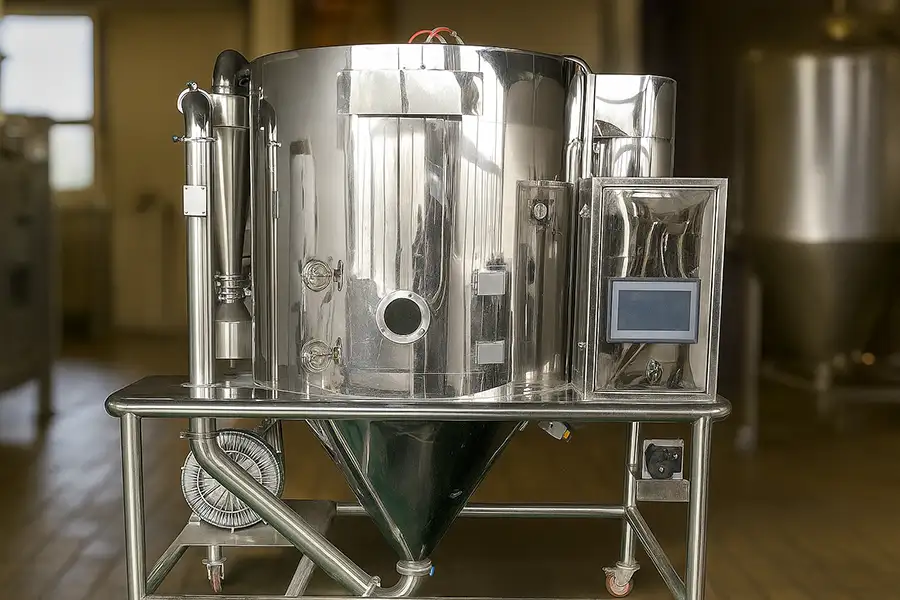
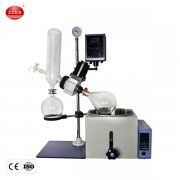
Spray drying is a fascinating technique widely used in the food industry to convert liquid or semi-liquid materials into dry powders. The process involves atomizing a liquid feed into tiny droplets, which are then exposed to hot air in a drying chamber. The moisture evaporates almost instantly, leaving behind fine, uniform powder particles. This technology is essential for producing products such as milk powder, coffee, egg powder, and flavorings.
According to a study by the Food Research Institute, spray drying can reduce moisture content from 70% to less than 5% within seconds, making it one of the fastest and most efficient drying methods available. This speed is critical for preserving the nutritional value and flavor of sensitive food materials.
How Does Spray Drying Work?
The process begins with a liquid feed that is pumped into a spray dryer through an atomizer. The atomizer breaks the liquid into fine droplets, which are then mixed with hot air. As the droplets travel through the drying chamber, the water evaporates, leaving behind solid particles. These particles are collected as powder at the bottom of the chamber.
The temperature, airflow, and droplet size are carefully controlled to ensure consistent quality. For example, milk powder production often uses inlet air temperatures of 180–200°C, while outlet temperatures are typically around 80°C.
Learn more about spray dryer vs dehydrator comparison
Applications in the Food Industry
Spray drying is used across a wide range of food applications:
-
Dairy products: milk, whey, and cheese powders.
-
Beverages: instant coffee, tea extracts, and fruit juice powders.
-
Flavors and colorants: encapsulating volatile compounds to preserve aroma and color.
-
Proteins and nutritional supplements: creating stable, easy-to-mix powders.
A report from the International Food Technology Association shows that over 50% of powdered food products worldwide are made using spray drying. This demonstrates its dominance and reliability in commercial food production.
Advantages of Spray Drying
Spray drying offers several benefits:
-
High-speed drying with minimal thermal degradation.
-
Excellent control over particle size and moisture content.
-
Enhanced product stability and shelf life.
-
Scalability for both lab-scale and industrial production.
Curious about how spray drying compares to freeze drying in preserving food nutrients? Let's explore this question.
Question: Which method better preserves food nutrients — spray drying or freeze drying?
Freeze drying generally retains more vitamins and enzymes because it operates at low temperatures. However, spray drying is much faster and more cost-effective for large-scale production. For heat-stable materials like milk or coffee, spray drying remains the preferred choice due to efficiency and economy.
Read about spray drying safety and food quality
Equipment and Technology
Modern spray drying machines are equipped with advanced control systems that monitor temperature, humidity, and particle formation. These features ensure consistent product quality and energy efficiency.
Based on data from the European Food Processing Equipment Association, energy consumption in modern spray dryers has been reduced by up to 25% through improved heat recovery systems and optimized airflow design.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its advantages, spray drying has some limitations. Heat-sensitive materials may lose certain nutrients or flavors during drying. Also, the initial investment in equipment can be significant for small-scale producers.
Question: How can small food manufacturers overcome the cost barrier of spray drying?
Small producers can collaborate with contract drying facilities or invest in compact lab-scale spray dryers. These smaller units are affordable and ideal for testing formulations before scaling up production.
Future of Spray Drying in Food Industry
The future of spray drying looks promising. With the rise of plant-based foods and functional powders, the demand for efficient drying technologies continues to grow. According to research from the Global Food Innovation Center, the spray drying market is expected to grow by 6.5% annually through 2030.
Question: Can spray drying be combined with other technologies for better results?
Absolutely. Hybrid systems combining spray drying with freeze drying or vacuum drying are being developed to balance nutrient retention and production speed. These innovations could redefine how food powders are manufactured globally.
Conclusion
Spray drying in the food industry is a cornerstone of modern food processing. It enables efficient transformation of liquids into powders while maintaining product quality and stability. As technology advances, spray dryers are becoming more energy-efficient, precise, and adaptable to diverse food materials.
For businesses seeking reliable drying solutions, investing in a high-quality spray dryer is a smart step toward innovation and sustainability.
Explore more about drying technologies and equipment at ZZKD Instrument Spray Dryer Guide.

 Products
Products