In the modern chemical and food processing industries, efficiency and consistency are key. One technology that has revolutionized the way powders are produced from liquids is the spray drying plant. This system combines precision engineering, thermal science, and material handling to create fine, uniform powders from liquid feedstock in seconds. But what exactly is spray drying, and why is it so widely used across industries?
What is a Spray Drying Plant?
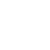
A spray drying plant is an industrial facility that converts liquid or slurry materials into dry powders by rapidly drying them with hot gas. The process involves atomizing the liquid into fine droplets, which are then exposed to a stream of hot air. The moisture evaporates almost instantly, leaving behind solid particles that can be collected as powder.
According to research conducted by the University of Cambridge, spray drying has become the preferred method for producing heat-sensitive materials such as pharmaceuticals, milk powder, and enzymes because it maintains product integrity while ensuring uniform particle size.
What makes spray drying different from traditional drying methods?
Traditional drying methods, such as oven or vacuum drying, rely on slow evaporation over time. Spray drying, on the other hand, occurs within seconds, minimizing thermal degradation and achieving more consistent results. It’s ideal for products where quality and uniformity are essential.
How Does a Spray Dryer Work?
The heart of any spray drying plant is the spray dryer machine. The process typically includes three main stages:
-
Atomization: The liquid feed is pumped through a nozzle or rotary atomizer, breaking it into tiny droplets.
-
Drying: These droplets are introduced into a hot air stream within the drying chamber. The moisture evaporates rapidly.
-
Collection: The dry powder particles are separated from the air using cyclones or filters and collected for packaging.
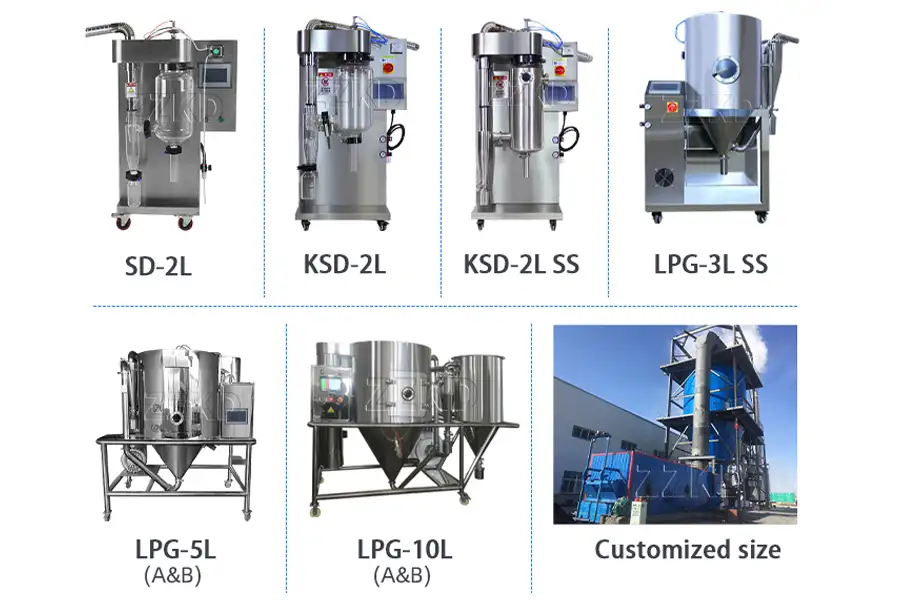

Modern spray drying plants are equipped with sophisticated control systems that monitor temperature, airflow, and droplet size to ensure optimal results. Advanced designs also include energy recovery systems to improve sustainability.
Is spray drying safe for food products?
Yes, it is. In fact, spray drying is commonly used in the food industry to produce milk powder, coffee, and flavorings. Studies from the Food Research Institute show that properly controlled spray drying preserves nutrients and flavor better than many alternative drying methods. You can read more about food safety and spray drying at
this detailed guide.
Applications of Spray Drying Plants
Spray drying is used across multiple sectors, including:
-
Food Industry: Production of milk powder, coffee, egg powder, and flavor encapsulation.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Drying of active ingredients and excipients for tablet formulation.
-
Chemicals: Creation of catalysts, polymers, and ceramic powders.
-
Biotechnology: Preservation of enzymes and probiotics.
For example, in dairy production, spray drying ensures consistent powder quality and long shelf life. In pharmaceuticals, it enables precise dosage control and improved solubility. The versatility of this technology is what makes it indispensable.
Advantages of Spray Drying Technology
There are several key benefits to using a spray drying plant:
-
Rapid drying time – typically less than 10 seconds.
-
Uniform particle size and shape.
-
Preservation of product quality and flavor.
-
Scalability from laboratory to industrial production.
-
Energy-efficient systems with heat recovery designs.
According to a report by the International Journal of Chemical Engineering, spray drying can reduce production costs by up to 40% compared to conventional drying methods, thanks to its speed and efficiency.
Can spray drying be used for sensitive materials?
Absolutely. Spray drying plants are designed to handle materials that are heat-sensitive or prone to degradation. By carefully controlling inlet and outlet temperatures, operators can ensure that delicate compounds like vitamins or enzymes remain active after drying.
Choosing the Right Spray Drying Plant
When selecting a spray drying plant, factors such as capacity, material compatibility, and energy efficiency must be considered. Laboratory-scale systems are ideal for R&D, while large industrial units serve mass production needs. For a deeper technical comparison, you can explore this guide to milk powder spray dryers.
Additionally, modern spray drying setups often integrate AI-based monitoring systems. According to a study by Stanford University, automation in process control can reduce human error by 25% and optimize energy consumption in continuous operations.
Future Trends in Spray Drying Plants
Innovation continues to drive the spray drying industry forward. With the rise of sustainable manufacturing and digital transformation, future plants will likely feature:
-
AI-powered predictive maintenance.
-
Renewable energy integration.
-
Real-time quality analytics.
-
Compact modular designs for flexible production.
These advancements will make spray drying more accessible, eco-friendly, and efficient, supporting industries from food production to pharmaceuticals.
Conclusion
The spray drying plant is more than just a piece of industrial equipment—it’s a cornerstone of modern manufacturing that bridges science and practicality. Its ability to transform liquids into powders quickly and efficiently has made it a key technology in global production lines. Whether for milk powder, chemicals, or pharmaceuticals, spray drying continues to set the standard for quality and performance.
To learn more about how spray drying compares to other drying methods, visit our article Is a Spray Dryer Better Than a Dehydrator?.

 Products
Products